Content
In this way, the ratio gives an early indication that a business might need to pay off existing debts before taking on more. In addition to reviewing the company’s financial statements, the times interest earned ratio is calculated to determine what proportion of income is used to cover interest expense. The formula for times interest earned is calculated by looking at the income statement and taking income before interest and taxes divided by the interest expense. High risk equals higher interest rates, while low risk equals lower interest rates. In some respects the times interest ratio is considered a solvency ratio because it measures a firm’s ability to make interest and debt service payments.
- A much higher ratio is a strong indicator that the ability to service debt is not a problem for a borrower.
- This is because it proves that it is capable of paying its interest payments when due.
- Additionally, the expansion the company is undergoing further suggests that it effectively reinvests its excess earnings in its growth and development.
- On the other side, it is essential to bear in mind, that EBIT is highly impacted by accounting standards and principles applied.
- A high TIE means that a company likely has a lower probability of defaulting on its loans, making it a safer investment opportunity for debt providers.
- Investors are looking forward to annual dividend payments of 4% plus an increase in the company’s stock price.
- Times Interest Earned ratio measures a company’s ability to honor its debt payments.
It can calculate the proportionate amount of earnings that can be used in the future, in order to cover expenses for interest. The current year value of 2.534 compared with the industry average of 3.425 indicates that management’s efforts are insufficient to improve the solvency of the company and reduce credit risk. However, a company with an excessively high TIE ratio could indicate a lack of productive investment by the company’s management. An overly high TIE suggests that the company may be keeping all of its earnings without re-investing in business development through research and development or pursuing positive NPV projects.
If you are a small business with a limited amount of debt, then the ratio is not all that important. GoCardless is authorised by the Financial Conduct Authority under the Payment Services Regulations 2017, registration number , for the provision of payment services. Learn more about how you can improve payment processing at your business today. In question, without factoring in any tax payments, interest, or other elements. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. Debt capacity refers to the total amount of debt a business can incur and repay according to the terms of the debt agreement.
How To Calculate Return On Assets Roa?
A company must regularly evaluate its ability to meet its debt obligations to ensure that it has enough cash to not only meet its debt but also operate its business. As obvious, a creditor would rather prefer a company with a high times interest ratio. Such a ratio can indicate the fact that the firm is able to afford the interest payments by the due date. Moreover, a higher ratio doesn’t have as many risks as a low one does, as the latter one brings credit risks. A higher interest earned ratio is favorable because it indicates that a company has enough earnings to pay its interest expense. A lower number shows that a company has insufficient earnings to meet its debt obligations in the long run. The higher a company’s times interest earned ratio, the more cash it has to cover its debts and invest in the business.
A Guide to Interest Coverage Ratio – Yahoo Finance
A Guide to Interest Coverage Ratio.
Posted: Mon, 12 Oct 2020 07:00:00 GMT [source]
However, with a high and stable TIE ratio, considering debt financing will be much preferred. It is less risky and easier to get a loan for a business with a high TIE ratio than otherwise. For a business owner, one of the questions to know the answer to is that what is times interest earned ratio? However, if you are not a business owner but a student of finance, this will enlighten you on the topic. The bigger the TIE ratio number, the more money the company has left over after paying off their interest expenses. If the number is less than one, then the company cannot pay off their debts and will surely head towards bankruptcy, to say nothing of their apparent incapacity to take on more debt by asking for a loan. To calculate the EBIT, we took the company’s net income and added back interest expenses and taxes.
How To Calculate The Times Interest Earned Ratio?
However, for a company with a high and stable ratio, there is room for growth as financial institutions and creditors will be willing to provide loans. The EBIT and interest expense are both included in a company’s income statement.
You can also calculate the times interest earned ratio using our online calculator. The reason to use EBIT in a formula is that interest expense is tax deductible, i.e., a company carries interest expense before paying income tax. A very high times interest ratio may be the result of the fact that the company is unnecessarily careful about its debts and is not taking full advantage of the debt facilities. Ensure that the company is in compliance with all the local laws that you are governed under. This will protect you against any fines that you might have to fork over for not complying. Apart from this, the business also needs to ensure that there are no chances for fraud to occur.
Increase Earnings
The current ratio is limited in that it measures a company or firm’s ability to meet its short-term obligation. While the times interest earned ratio measures its ability to fulfill long-term debts.
Let us take the example of Apple Inc. to illustrate the computation of Times interest earned ratio. As per the annual report of 2018, the company registered an operating income of $70.90 billion while incurring an interest expense of $3.24 billion during the period. Calculate the Times interest earned ratio of Apple Inc. for the year 2018.
Accountingtools
The better the ratio, it implies that the company is in a decent position financially, which means that they have the ability to raise more debt. But it should not be the only metric that lenders should use to decide if the company is worth lending to. There are so many other factors like the debt-equity ratio and the market conditions which should be used to assess before lending. The times interest earned ratio quantifies how well a company can handle its debt obligations without fail. It is a measure of the interest expenses of a company in terms of its income. A company with a low ratio is at credit risk and will find obtaining a loan difficult.
The interest expense towards debt and lease was $1.98 billion and $0.35 billion respectively. Calculate the Times interest earned ratio of Walmart Inc. for the year 2018 if the taxes paid during the period was $4.60 billion. Here’s everything you need to know, including how to calculate the times interest earned ratio. The formula for a company’s TIE ratio consists of dividing the company’s EBIT by the total interest expense on all debt securities. Also, for developing companies, knowing for how long the current income can handle possible debts will help in prioritizing growth. Whether to gain more assets, to source for other means of income, invest in opportunities, or maintain the trend.
What Does a High-Times Interest Earned Ratio Signify for a Company’s Future? – Investopedia
What Does a High-Times Interest Earned Ratio Signify for a Company’s Future?.
Posted: Sat, 25 Mar 2017 19:27:46 GMT [source]
I want to ask, if the company given the times-interest earned ratio is 4.2, an annual expenses $30,000 and its pay income tax equal to 28% of earning before tax. Times interest earned ratio is very important from the creditors view point. The companies with weak ratio may have to face difficulties in raising funds for their operations. A creditor has extracted the following data from the income statement of PQR and requests you to compute and explain the times interest earned ratio for him.
A TIE ratio of 5 means you earn enough money to afford 5 times the amount of your current debt interest — and could probably take on a little more debt if necessary. In a perfect world, companies would use accounting software and diligence to know where they stand, and times interest earned ratio formula not consider a hefty new loan or expense they couldn’t safely pay off. But even a genius CEO can be a tad overzealous, and watch as compound interest capsizes their boat. The Times Interest Earned Ratio Calculator is used to calculate the times interest earned ratio.
Times Interest Earned Ratio Calculation Example
Commonly, the more consistent that a company’s earnings are, the more likely it is the company has more debt as a percentage of their total capital gain. This means that the company relies on various credits to fund its primary operations for revenue generation. A company that has a history of generating consistent earnings is a better credit risk for lenders and long-term investors than companies without a history of consistent earnings.
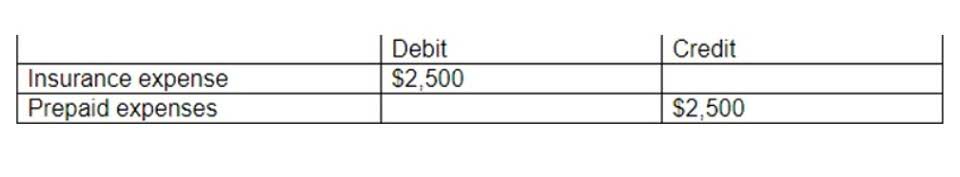
The statement shows $50,000 in income before interest expenses and taxes. When a company can generate consistent income, this value becomes the company’s consistent earnings.
The times interest earned ratio indicates the extent of which earnings are available to meet interest payments. When the interest coverage ratio is smaller than one, the company is not generating enough cash from its operations EBIT to meet its interest obligations. For prospective lenders, a high interest expense compared to to your earnings can be a red flag. If the water is filling your glass faster than you can drink it, it’s fair to say you should not be given more — more debt means more interest. A bank or financial institution must charge a business interest; they must get something in return for loaning money.
- Once a company establishes a track record of producing reliable earnings, it may begin raising capital through debt offerings as well.
- Otherwise known as the interest coverage ratio, the TIE ratio helps measure the credit health of a borrower.
- Editorial content from The Blueprint is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different analyst team.
- However, having an excessively high value could mean low re-investment by the company, which could be toxic in the long-run.
- Dummies helps everyone be more knowledgeable and confident in applying what they know.
Times Interest Earned or Interest Coverage is a great tool when measuring a company’s ability to meet its debt obligations. When the interest coverage ratio is smaller than 1, the company is not generating enough cash from its operations EBIT to meet its interest obligations. The Company would then have to either use cash on hand to make up the difference or borrow funds. Typically, it is a warning sign when interest coverage falls below 2.5x. Times interest earned or Interest Coverage ratio is a measure of a company’s ability to honor its debt payments. It may be calculated as either EBIT or EBITDA divided by the total interest payable. Times interest earned or interest coverage ratio is a measure of a company’s ability to honor its debt payments.
Our second example shows the impact a high-interest loan can have on your TIE ratio. Looking for the best tips, tricks, and guides to help you accelerate your business? Beginner’s Guides Our comprehensive guides serve as an introduction to basic concepts that you can incorporate into your larger business strategy. Construction Management CoConstruct CoConstruct is easy-to-use yet feature-packed software for home builders and remodelers. This review will help you understand what the software does and whether it’s right for you. Appointment Scheduling 10to8 10to8 is a cloud-based appointment scheduling software that simplifies and automates the process of scheduling, managing, and following up with appointments.
Which of the following is the numerator used in calculating the times interest earned ratio?
The numerator in the times interest earned ratio is: net income plus interest expense.
If your business has debt and you are looking to take on more doubt, then the interest coverage ratio will provide your potential lenders with an understanding of how risky a business you are. It will tell them whether you would pay back the money that they are lending you. Usually, a higher times interest earned ratio is considered to be a good thing. But if the balance is too high, it could also mean that the company is hoarding all the earnings without putting them back into the company’s operations.

While it is easier said than done, you can make the interest coverage ratio better by improving your revenue. The company will be able to increase its sales which will help boost earnings before interest and taxes. Businesses and organizations that have consistent earnings commonly have a higher borrowing rate. This means that creditors are more likely to risk lending to a company with consistent earnings because its history shows it generates enough consistent earnings to cover its long-term debt obligations. Even though a higher times interest earned ratio is more favorable, it can be too high. For instance, if an organization’s times interest earned ratio far exceeds the industry average, it can show misappropriation of earnings. This means that the organization is paying down its debt too quickly without using its excess income for reinvesting in the business through new projects or expansion.
Said differently, the company’s income is four times higher than its yearly interest expense. If the company could find out areas where costs could be cut, it will significantly add to their bottom line. Streamlining their operations and looking for ways to cut costs on a 360-degree front will make it work.
If you have three loans that are generating interest and don’t expect to pay those loans off this month, you have to plan to add to your debts based these different interest rates. The higher the TIE, the better the chances you can honor your obligations.
For example, if a company owes interest on its long-term loans or mortgages, the TIE can measure how easily the company can come up with the money to pay the interest on that debt. To ensure that you are getting the real cash position of the company, you need to use EBITDA instead of earnings before interests and taxes. Just like any other accounting ratio, it is best advised not to compare your score against other businesses but only with those who are in the same industry as you.
With that said, it’s easy to rack up debt from different sources without a realistic plan to pay them off. If you find yourself with a low times interest earned ratio, it should be more alarming than upsetting.
Author: Elisabeth Waldon






Be the first to comment